Gangrene Wound Care
Diabetics are most prone to foot gangrene because they typically have poor circulation or nerve damage, which can lead to loss of blood supply. Diabetic neuropathy, or nerve loss, affects the nerves of the feet and legs causing a diminished ability to perceive pain, excessive heat, cold, vibration, or excessive pressure.
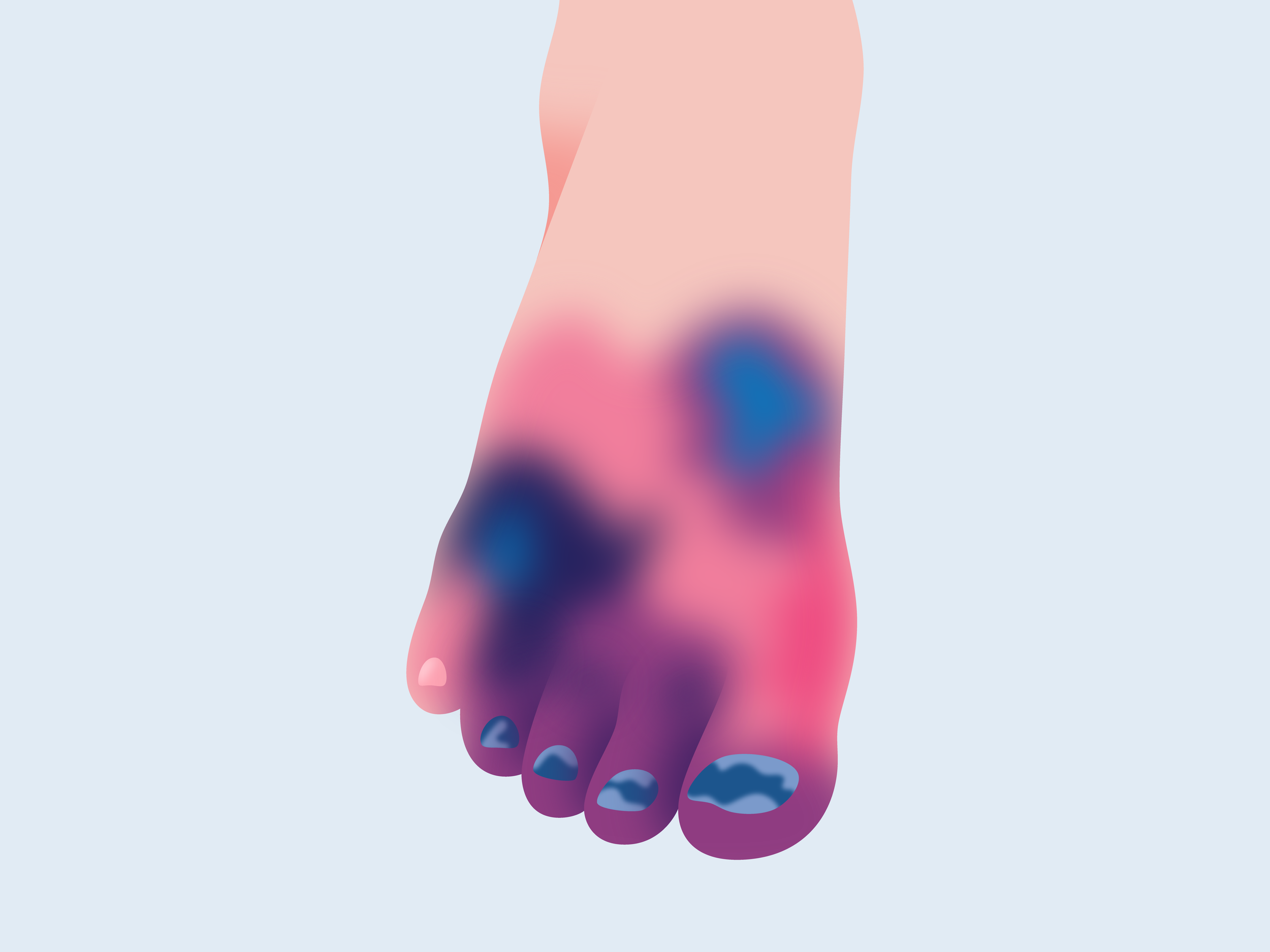
What is Gangrene?
Gangrene usually occurs after the blood supply to your foot is lost. Bacterial infections of open sores or ulcers also can lead to gangrene.
Diabetics are most prone to foot gangrene because they typically have poor circulation or nerve damage, which can lead to loss of blood supply. Diabetic neuropathy, or nerve loss, affects the nerves of the feet and legs causing a diminished ability to perceive pain, excessive heat, cold, vibration, or excessive pressure.
Any sudden onset of foot or leg pain accompanied by lower skin temperature and skin color changes may indicate a sudden blockage of blood flow to the legs.
Surgical intervention is necessary, followed by oxygen treatment and intravenous antibiotics.
Some flesh-eating bacteria (hemolytic streptococcus) can cause intense local heat, redness, swelling, fever, and weakness. The infection can start with a small abrasion or injury. This condition requires immediate medical treatment and can result in amputation and/or death.