Wound Care.
Non-healing wounds can present serious health risks and often require wound care. Treatment of underlying problems is the first step in a healing process whose goals are to alleviate pain, speed recovery, regain mobility, and fully heal the wound.
Non-Healing Wounds
Patients with peripheral vascular disease (PVD) often have non-healing wounds in their extremities. Blood flow, oxygen, and nutrients are necessary for wounds to heal. Patients with PVD have decreased blood flow to their arms or legs, which promotes poor healing. By treating the underlying vascular problem, wounds can be treated effectively and heal much faster.
What are the risk factors for Non-Healing Wounds?
There are a multitude of risk factors that can contribute to the development of non-healing wounds.
The following list outlines the most common risk factors for non-healing wounds.
Advanced peripheral vascular disease (PVD).
Kidney failure.
Venous insufficiency.
Hypertension.
Diabetes.
Lymphedema.
Inflammatory diseases, such as vasculitis, lupus, or scleroderma.
Smoking.
Inactivity, resulting in pressure from lying in one position for too long.
Cancer.
Infection.
How are Wounds diagnosed?
There are three main types of wounds on the lower extremities: venous stasis ulcers, neurotrophic ulcers, and arterial ulcers. A thorough examination of the wound will be completed and other diagnostic testing may be done to determine any underlying problems that need to be corrected.
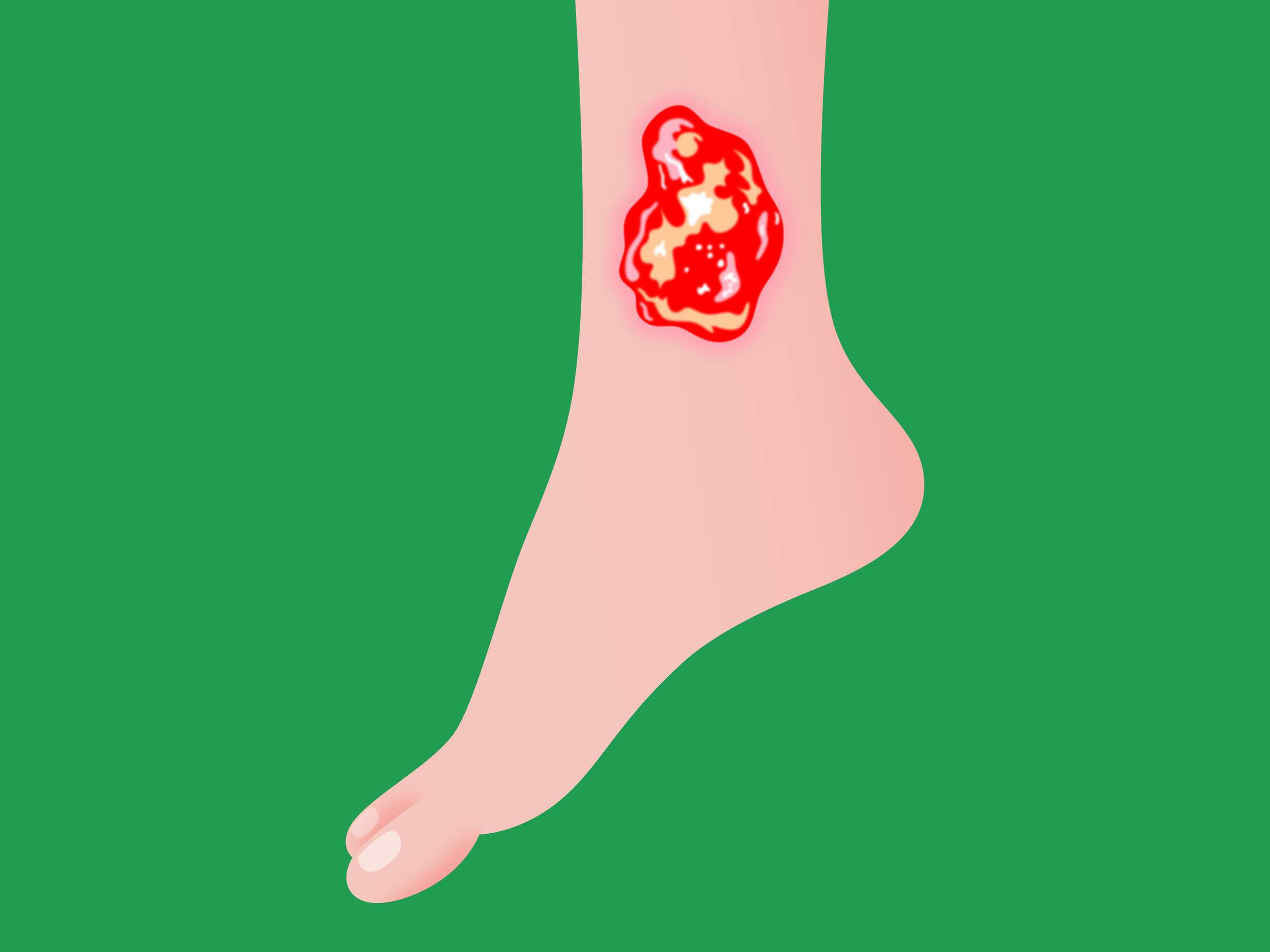
Venous Stasis Ulcers
These are usually found below the knee on the inner part of the leg just above the ankle. They usually have irregular borders, are red in color, are often covered with yellowish tissue, and drainage may be present. The skin around this type of ulcer is discolored and swollen with a shiny, tight appearance.
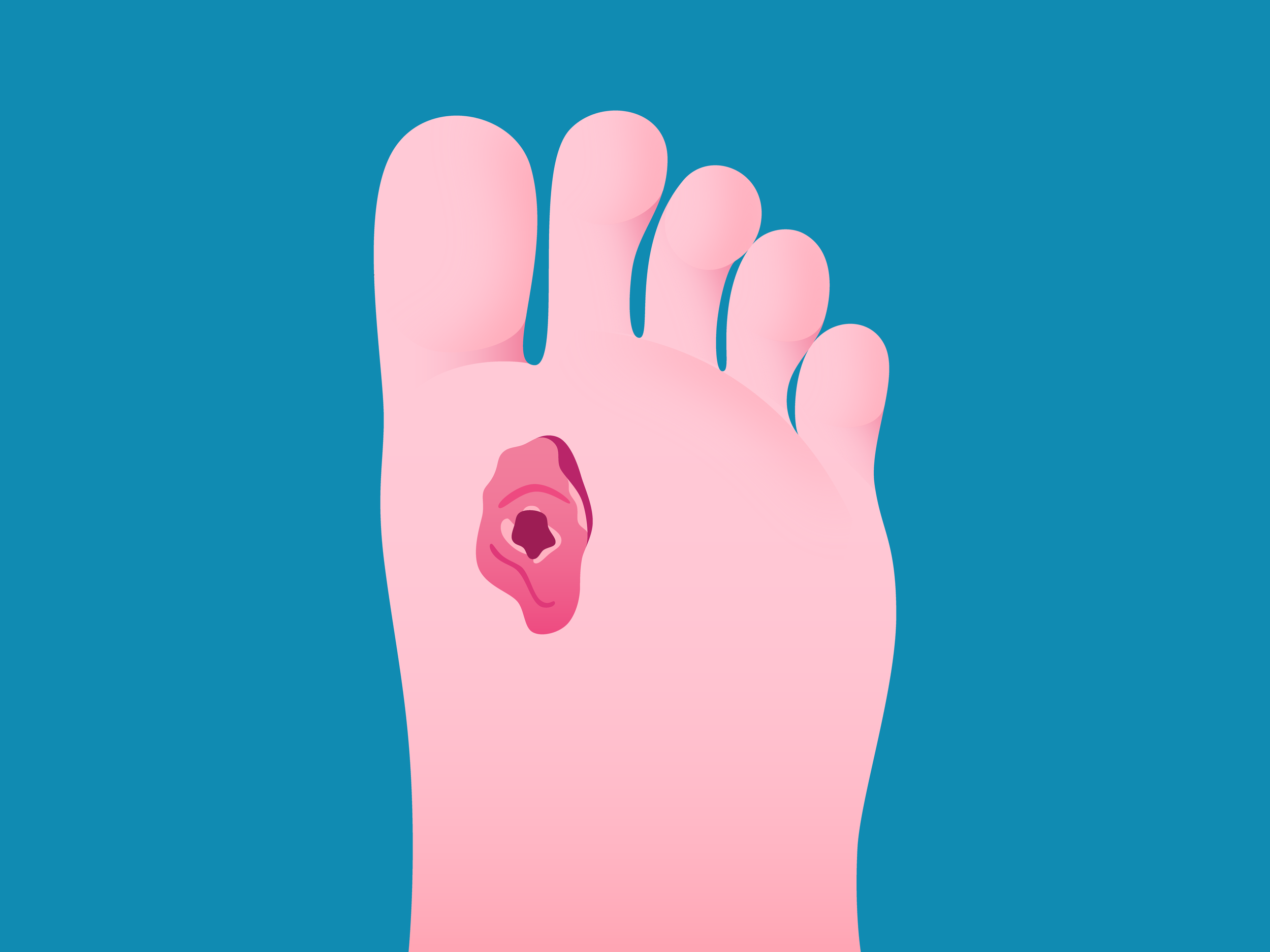
Neurotrophic Ulcers
These are usually found at areas of increased pressure points on the bottom of the feet, but can occur anywhere on the foot. The base appears pinkish red or brownish/black, with punched out borders and calloused surrounding skin.
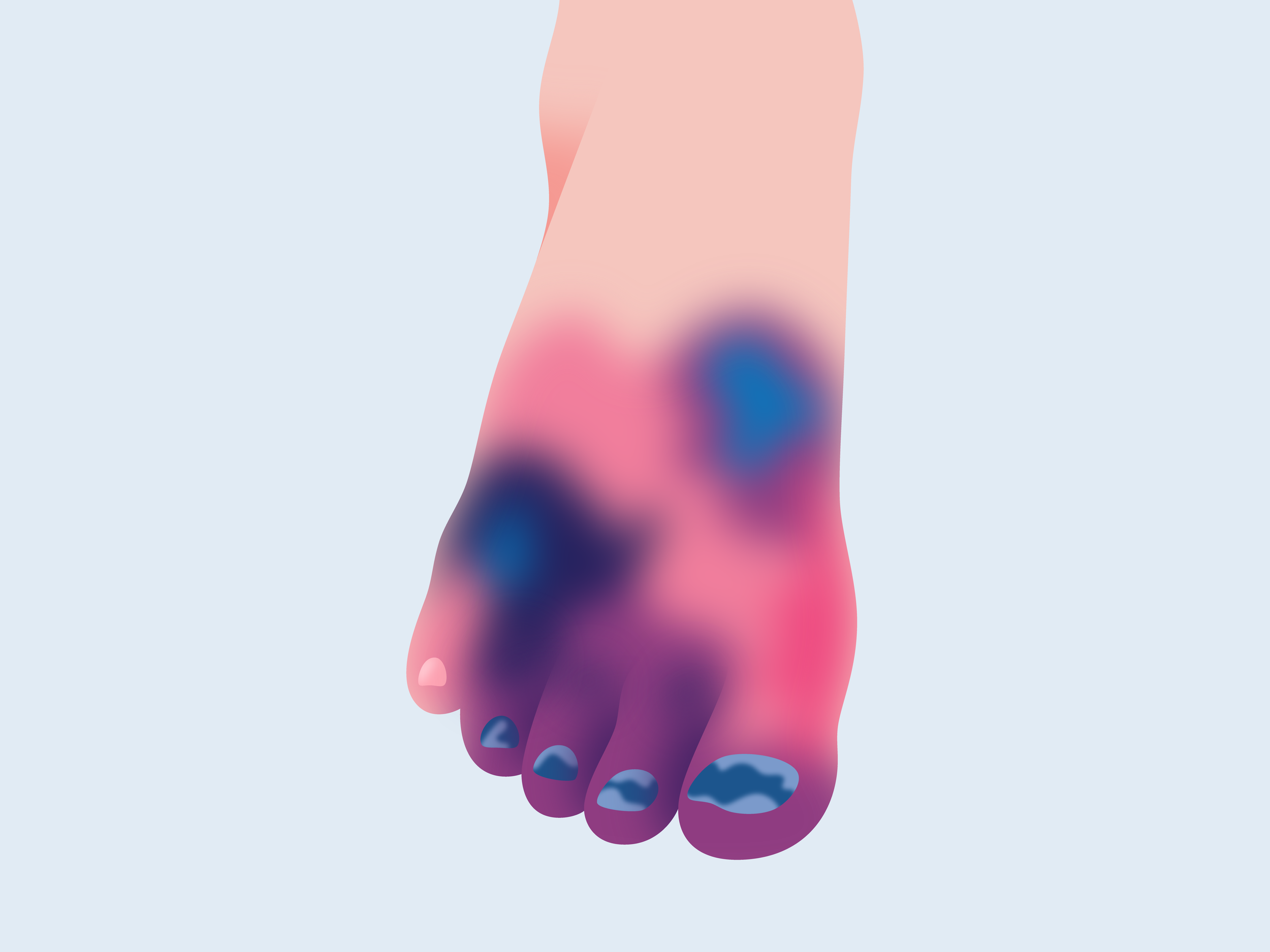
Arterial Ulcers
These are usually found on the feet, particularly on the heels or toes and nail bed. The coloration can be yellow, brown, grey, or black, with punched out borders and the surrounding skin is often swollen and red. The entire leg will turn red when dangled and pale white when elevated due to the lack of blood flow. These wounds are very painful.
What are my Wound Care Treatment options?
Wound care begins with treating any underlying problems contributing to non-healing. This would include treating any vascular problems that could be impeding blood flow to the affected leg or arm. This may be done by angioplasty/stenting, endovascular, or bypass surgery.
The goals of wound care are to alleviate pain, speed recovery, regain mobility, and heal the wound fully. Wound care treatment after revascularization includes:
Debridement
During this procedure, the dead or infected tissue of a wound is removed to reduce the number of microbes and substances that may be inhibiting healing.
Antibiotics
Medications that may be used to treat an infection in a wound if present. These may be in topical or oral form.
Topical Wound Care Therapies
There are a multitude of applications to help heal a wound so it can heal from the inside out. The type will depend upon the type of wound, location, and extent of damage. They include moist to moist or moist to dry dressings, hydrogels/hydrocolloids, alginate, collagen wound dressings, topical debriding agents, antimicrobial dressings, composite dressings, and synthetic skin substitutes.
Compression Dressings
This therapy involves wearing multi-layer compression wraps or wrapping an ACE bandage. These are generally used for venous stasis ulcers to minimize swelling.
Prosthetics or Orthotics
These are devices available to help restore someone back to their normal lifestyle and level of functioning.
Skin Grafts
During this procedure, healthy skin from one part of the body or synthetic material is used to cover open wound areas. This can promote faster healing of a wound and help in restoring a more normal appearance.